The 5G specification, seen as an upgrade from the prevailing 4G networks, defines options to interconnect with non-cellular technologies, such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. LoRa protocols, in turn, interconnect with cellular IoT at the data management level (application layer), providing robust long-range coverage of up to 10 miles. Compared with 5G, LoRaWAN is a relatively simple technology built from the ground up to serve specific use cases. It also entails lower costs, greater accessibility, and enhanced battery performance.
Nonetheless, this is not to say LoRa-based connectivity can be seen as a 5G replacement. On the contrary, it instead enhances and extends the potential of 5G, supporting implementations that use the already deployed cellular network infrastructure and don’t require ultra-low latency.
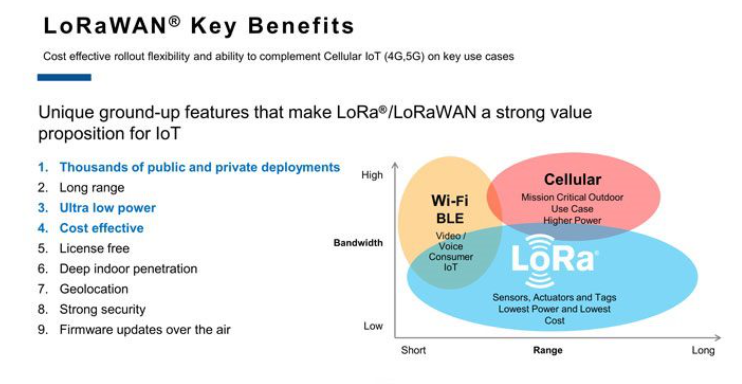
Key areas for LoRaWAN application in IoT
Designed to wirelessly connect battery-operated devices to the internet, LoRaWAN is a perfect fit for IoT sensors, trackers, and beacons with limited battery power and low data traffic requirements. The intrinsic characteristics of the protocol make it an ideal choice for a wide variety of applications:
Smart metering and utilities
LoRaWAN devices are also proving efficient in smart utility networks, which leverage intelligent meters often located in places that are beyond the reach of sensors operating in 5G networks. By ensuring the required access and range, LoRaWAN-based solutions allow for remote daily operations and the collection of data that turns information into action, without manual interventions of the field technician staff.
Post time: Dec-08-2022







