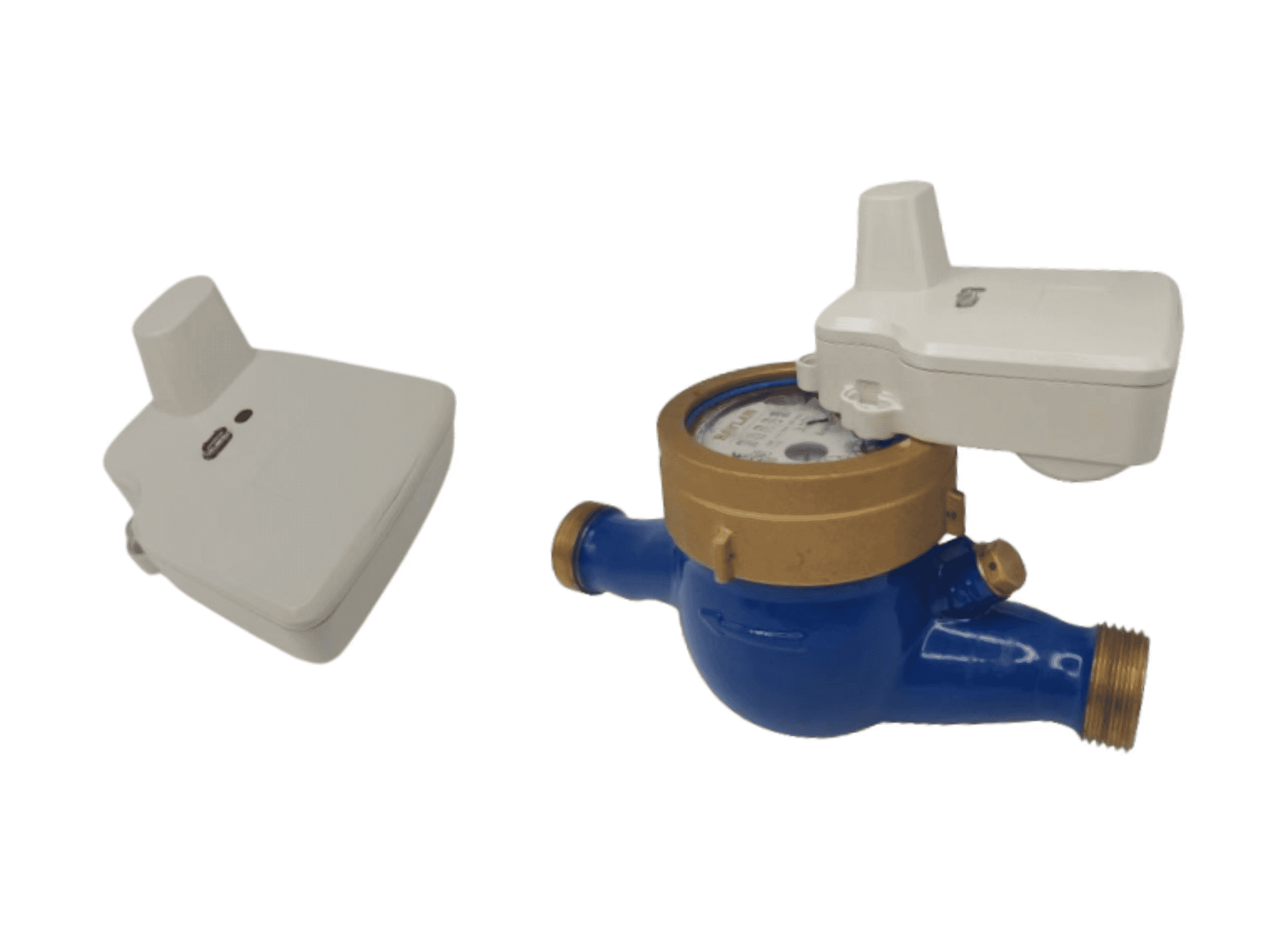
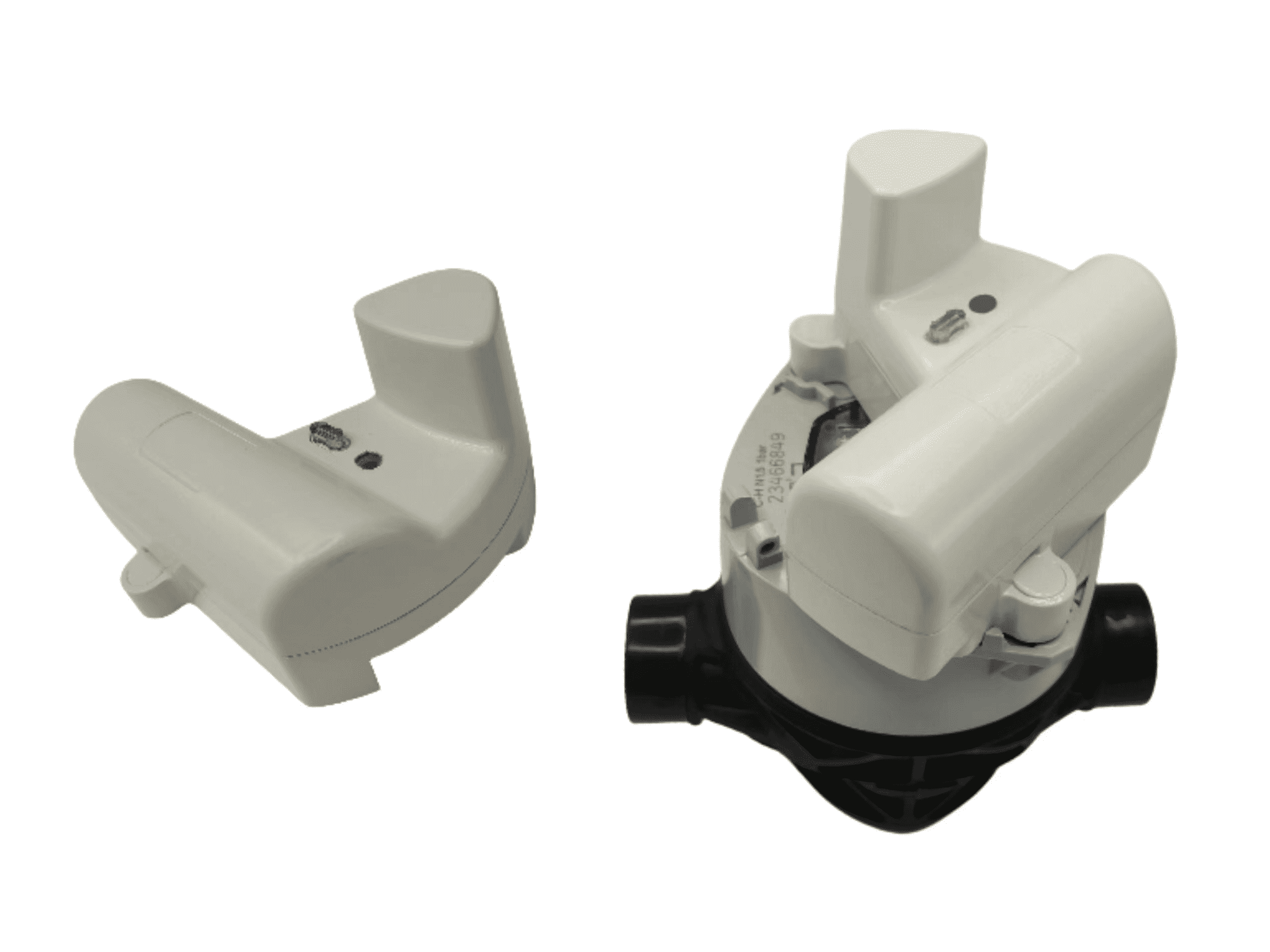
Water meter reading is a crucial process in managing water usage and billing in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. It involves measuring the volume of water consumed by a property over a specific period. Here’s a detailed look at how water meter reading works:
Types of Water Meters
- Mechanical Water Meters: These meters use a physical mechanism, such as a rotating disk or a piston, to measure water flow. The movement of water causes the mechanism to move, and the volume is recorded on a dial or counter.
- Digital Water Meters: Equipped with electronic sensors, these meters measure water flow and display the reading digitally. They often include advanced features like leak detection and wireless data transmission.
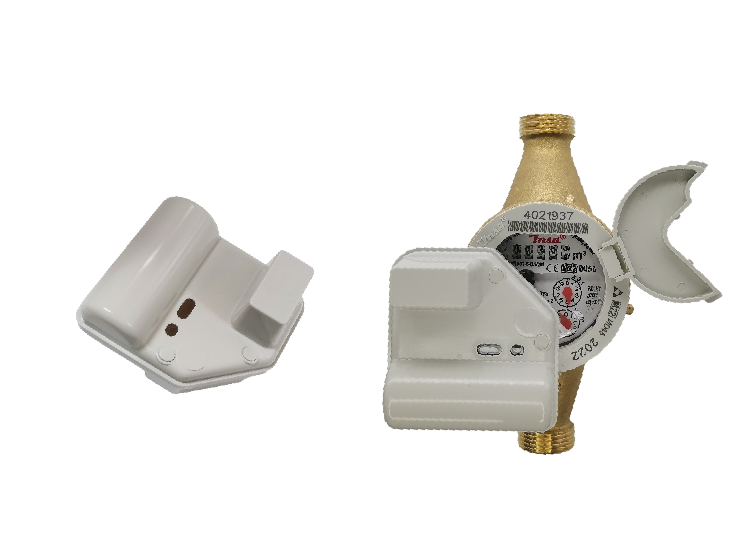
- Smart Water Meters: These are enhanced digital meters with integrated communication technology, allowing remote monitoring and data transmission to utility companies.
Manual Meter Reading
- Visual Inspection: In traditional manual meter reading, a technician visits the property and visually inspects the meter to record the reading. This involves noting the numbers displayed on the dial or digital screen.
- Recording the Data: The recorded data is then either written down on a form or entered into a handheld device, which is later uploaded to the utility company’s database for billing purposes.
Automated Meter Reading (AMR)
- Radio Transmission: AMR systems use radio frequency (RF) technology to transmit meter readings to a handheld device or a drive-by system. Technicians collect the data by driving through the neighborhood without needing to access each meter physically.
- Data Collection: The transmitted data includes the meter’s unique identification number and the current reading. This data is then processed and stored for billing.
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
- Two-Way Communication: AMI systems use two-way communication networks to provide real-time data on water usage. These systems include smart meters equipped with communication modules that transmit data to a central hub.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Utility companies can remotely monitor water usage, detect leaks, and even control the water supply if necessary. Consumers can access their usage data through web portals or mobile apps.
- Data Analytics: The data collected via AMI systems is analyzed for usage patterns, helping in demand forecasting, resource management, and identifying inefficiencies.
How Meter Reading Data is Used
- Billing: The primary use of water meter readings is to calculate water bills. The consumption data is multiplied by the rate per unit of water to generate the bill.
- Leak Detection: Continuous monitoring of water usage can help in identifying leaks. Unusual spikes in consumption can trigger alerts for further investigation.
- Resource Management: Utility companies use meter reading data to manage water resources efficiently. Understanding consumption patterns helps in planning and managing supply.
- Customer Service: Providing customers with detailed usage reports helps them understand their consumption patterns, potentially leading to more efficient water use.
Post time: Jun-17-2024